
ARTON PROGRAM - The therapeutic power of the group
Creative projects involving group work - general musical performance or group painting, collage, sculpture - are useful in helping to explore and strengthen social...
Emotional support for children with medical conditions
Juliann Garey
When a child has a medical condition, families are, naturally, focused on finding and maintaining the most effective care. Concerned about the child’s physical well-being, it’s easy to overlook the emotional toll a chronic illness can take.
Whether it’s a food allergy or asthma — conditions that require long-term vigilance — or a cancer diagnosis, kids may need help to handle it in the healthiest possible way. Parents, too, may need help processing a child’s condition and their own feelings about it. In fact, parents are often more upset than their children, and if they are struggling it can impact their child as well.
The most common issues kids with medical diagnoses face are depression and anxiety, says clinical psychologist Lauren Latella, PhD. And they can be triggered “by anything that’s going to spark kids to start thinking about themselves differently, as having a limitation.”
Chronic medical illnesses can disrupt:
As a result of these disruptions in their day-to-day lives, kids with medical conditions often feel left out or self-conscious. Depending on their age, these feelings can lead to behavioral issues, anxiety and depression.
Not all children will struggle, however. Some, especially younger children, may not fully understand what is wrong. If the people around them help them feel comforted and secure, they may be resilient and act like any other child. Some factors that make a child more likely to struggle are:
In some situations, children may be less affected than their parents. “Parents may have a really hard time and that can set the tone for the recovery,” notes Jamie Howard, PhD, a psychologist at the Child Mind Institute. That’s because children can pick up on when a parent is upset, and it can make them upset, too. If they’re very young, they may feel confused and anxious because they might not understand why their parent is worried. Or if a parent is feeling like their child is very fragile or in danger, the child may start thinking that, too, and it can affect their self-identity and ability to be resilient. Parents might also have a hard time setting limits, which can make kids feel anxious and start acting out.
Some parents can even develop post-traumatic stress disorder. “Parents can get in this mode where all they do is focus on their child and all the many doctors for their children and getting their children healthy,” says Dr. Howard. “And then months after it seems like things have calmed down and their child is okay, they’re not functioning because they’ve been in fight or flight mode.”
For parents who need help processing their own feelings, reaching out to a mental health professional can be an important first step to feeling secure, both for them and their child.
Many parents want to protect their children from the difficult and painful realities of having a medical illness. They may avoid talking about the medications or the specifics of the illness — or sometimes even the name of the illness — because they’re afraid it’s going to make the child more frightened. But, says Dr. Latella, “not talking about things at a developmentally appropriate level actually causes more worry and leads to depressive symptoms later on.” If you’re not sure how much information to share with a child, a mental halth professional can help you understand what’s developmentally appropriate.
Dr. Howard recommends to always pair that description with an explanation of what you are doing to help the child get better in order to help the child feel empowered.
When kids get to be older, they may want or need to take more control over their treatment, but they may also be less adherent. “Twelve to eighteen is the critical period of adolescence in normal development where kids are trying to get more autonomy,” Dr. Latella says. “So parents may see some oppositionality in the form of family conflict.”
The best way for parents to respond to this behavior is by involving the adolescent as much as possible in decision making and conversations, so they can feel like they have some control over their treatment. Parents should also set clear, consistent messages about what is expected of the adolescent to manage their behaviors. Dr. Latella suggests making contracts with teens about medication adherence and other aspects of managing their illness.
And then to do your best to give your child as normal a life as you possibly can. This includes continuing to set the same behavioral expectations and boundaries you would with a healthy child. If kids are medically able, they need to complete school work and continue to help around the house in the same way their healthy siblings do. It’s up to parents to make sure a child with a diagnosis doesn’t automatically get a “pass” just because of their medical condition. “Parents should be mindful of when they are becoming overprotective or too lax,” says Dr. Latella. “It is important to give any child structure; therefore, maintaining the family routine prior to the illness diagnosis is important.”
Younger kids and adolescents will most likely have different reactions to the stress brought on by a medical condition and everything that goes along with it since they understand illness in a different way as they get older.
Younger kids (between the ages of three and ten) who worry about their condition, Dr. Latella explains, are more likely to exhibit behavioral symptoms, like being oppositional and other kinds of acting out. “It’s normal to expect some of that in the beginning,” says Dr. Latella. “But if after a few weeks those behaviors still persist then that’s when it becomes more problematic.”
Warning signs to look out for in kids ages three to ten include:
In adolescents, stress manifests more as depression and disruption of interpersonal relationships. Warning signs in kids ages ten to eighteen include:
There is a lot that clinicians can do to mitigate the experience of having a chronic medical condition and it all starts with talking opening and honestly with your child at a level that is appropriate for their age. For younger kids, Dr. Latella says mental health clinicians may work with younger kids in the following ways:
For teens who are more prone to depression and anxiety than behavioral symptoms, the therapy is different. Therapy for older kids focuses on:
Article re-posted from https://childmind.org/

Creative projects involving group work - general musical performance or group painting, collage, sculpture - are useful in helping to explore and strengthen social...
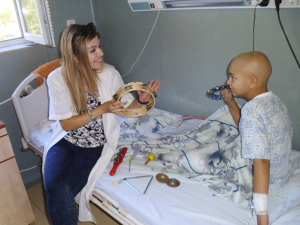
In the ARTON Program our team of oncopsychologists, art therapists and music therapists develops the process of children's creativity as a process of...

In ARTON sessions, creating a piece of music or a song is an emotional experience of coping and satisfaction for the participating children. They make friends with...

Painting provides patients with a spontaneous, plastic method of depicting thoughts and experiences. Painting with paints is not as structured as with pencil or...










