
ARTON PROGRAM - The therapeutic power of the group
Creative projects involving group work - general musical performance or group painting, collage, sculpture - are useful in helping to explore and strengthen social...
According to a study conducted by the Harvard Medical School, close to 8 percent of adolescents display anger issues that qualify for lifetime diagnoses of intermittent explosive disorder. Anger issues aren’t limited to teens, and it’s important to understand anger symptoms, causes and effects if you suspect you are, or someone you know is, suffering from an anger disorder.
Individuals who have trouble controlling anger or who experience anger outside of a normal emotional scope can present with different types of anger disorders. Different experts have published contradicting lists of anger types, but some widely accepted forms of anger include:
People experiencing passive anger may not even realize they are angry. When you experience passive anger, your emotions may be displayed as sarcasm, apathy or meanness. You might participate in self-defeating behaviors such as skipping school or work, alienating friends and family, or performing poorly in professional or social situations. To outsiders, it will look like you are intentionally sabotaging yourself, although you may not realize it or be able to explain your actions.
Because passive anger may be repressed, it can be hard to recognize; counseling can help you identify the emotions behind your actions, bringing the object of your anger to light so you can deal with it.
Individuals who experience aggressive anger are usually aware of their emotions, although they don’t always understand the true roots of their ire. In some cases, they redirect violent anger outbursts to scapegoats because it is too difficult to deal with the real problems. Aggressive anger often manifests as volatile or retaliatory anger and can result in physical damages to property and other people. Learning to recognize triggers and manage anger symptoms is essential to dealing positively with this form of anger.
A leading cause of anger is a person’s environment. Stress, financial issues, abuse, poor social or familial situations, and overwhelming requirements on your time and energy can all contribute to the formation of anger. As with disorders such as alcoholism, anger issues may be more prevalent in individuals who were raised by parents with the same disorder. Genetics and your body’s ability to deal with certain chemicals and hormones also play a role in how you deal with anger; if your brain doesn’t react normally to serotonin, you might find it more difficult to manage your emotions.
Losing your cool from time to time doesn’t mean you have an anger management problem. Mental health professionals look at trends in your behavior, emotional symptoms and physicalsymptoms to diagnose an anger disorder.
You might think the emotional symptom of anger-related problems are limited to anger, but a number of emotional states could indicate that you are failing to deal with anger in a positive and healthy fashion. Constant irritability, rage and anxiety are possible emotional symptoms.
If you feel overwhelmed, have trouble organizing or managing your thoughts or fantasize about hurting yourself or others, you could be experiencing an anger disorder or another issue. Don’t wait for these emotions to take control of your life; maintain control by calling our hotline today at . Representatives are available to listen and offer advice 24/7.
Strong emotions often bring about physical changes to the body, and anger is no exception. Letting anger issues go unaddressed can put your overall health at risk. Some physical symptoms of anger-related problems include:
Unresolved anger issues lead to anxiety, which can have long-term effects on your life. Immediate effects of anxiety might include dizziness, rapid breathing, nausea, muscle pain, muscle tension, headaches, and problems with concentration and memory. Such symptoms can make it difficult to perform routine tasks and can add to generalized anger about life.
Long-term anxiety can pose dangerous risks to your physical and emotional states. Individuals who suffer from long bouts of anxiety can be at a greater risk for strokes. Serious memory loss, chronic sleep disorders and relationship issues can also develop. Before your anger and anxiety wreak havoc with your entire life, find out what you can do to stop the cycle by calling .
A number of self-assessment tests are available online to help you to recognize any anger and anxiety issues you may be experiencing. If you take an online test, it’s a good idea to ensure that it was written and published by someone recognized as an expert in the mental health field.
Even if the test is offered by a reputable organization, you should never allow a self-diagnosis or an online test to direct your course of treatment. Individuals who think they might be suffering from anger issues should speak to professional counselors, family physicians or volunteers from local healthcare organizations.
Mental health professionals recommend counseling, group therapy sessions and anger management classes as treatment options for anger disorders. In some cases, medication may be helpful in controlling emotions and chemical reactions in the body that lead to uncontrollable anger.
The type of drugs prescribed will depend on individual circumstances and take into account other diagnoses. Possible options include:
According to reports, up to 50 percent of patients on lithium experience renal-related side effects.These effects areusually reversed by medical care or discontinuation of the drug but serve as a good illustration of why you should only take medication for anger symptoms while under the care of a physician. Other side effects for different anger-related medications include:
It’s important to understand whether your anti-anger drug could be addictive. Addiction to the drug will depend on your own personality, your body’s chemical makeup and the drug itself. Discuss the dangers associated with dependence and withdrawal with your healthcare provider, and make sure you follow instructions regarding the dosage closely. If you experience side effects, find yourself wanting more of the medication, or are unable to stop taking the medication, talk to your doctor immediately.
To reduce the chance of medication overdose, always follow dosage requirements. If you experience health issues while taking the medication, report them immediately to the prescribing physician because physical symptoms could be an indicator that your dose is too high.
Depression and anger go hand in hand and can cause a revolving cycle that’s hard to break. Lashing out in anger can lead to alienation and feelings of guilt, which can lead to depression. Long-term depression can make it difficult to handle emotions, increasing the likelihood of anger outbursts. Often, the only way to break this cycle is to seek professional help.
Drug and alcohol addictions can decrease your ability to deal with anger. It’s important to seek treatment options that deal with emotional and physical issues related to your disorder. A treatment program that addresses anger without dealing with addiction leaves you vulnerable to emotional issues in the future.
Likewise, attending a group to discuss your addiction without mentioning your struggle with anger makes it likely you’ll use drugs or alcohol to deal with emotional pain in the future.
The first step to taking control of your life is to seek help for your anger-related problem. Treatment resources include inpatient facilities, outpatient programs, individual and group therapy, and medication. Call us today at to find out what you can do to start on the path to recovery today. Learning about anger symptoms, causes and effects will help you address your disorder in a healthy and positive way.

Creative projects involving group work - general musical performance or group painting, collage, sculpture - are useful in helping to explore and strengthen social...
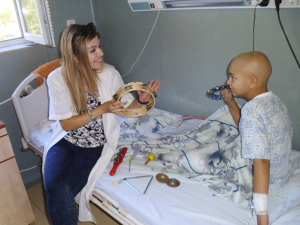
In the ARTON Program our team of oncopsychologists, art therapists and music therapists develops the process of children's creativity as a process of...

In ARTON sessions, creating a piece of music or a song is an emotional experience of coping and satisfaction for the participating children. They make friends with...

Painting provides patients with a spontaneous, plastic method of depicting thoughts and experiences. Painting with paints is not as structured as with pencil or...










