
ARTON PROGRAM - The therapeutic power of the group
Creative projects involving group work - general musical performance or group painting, collage, sculpture - are useful in helping to explore and strengthen social...

We don’t always eat just to satisfy physical hunger. Many of us also turn to food for comfort, stress relief, or to reward ourselves. And when we do, we tend to reach for junk food, sweets, and other comforting but unhealthy foods. You might reach for a pint of ice cream when you’re feeling down, order a pizza if you’re bored or lonely, or swing by the drive-through after a stressful day at work.
Emotional eating is using food to make yourself feel better—to fill emotional needs, rather than your stomach. Unfortunately, emotional eating doesn’t fix emotional problems. In fact, it usually makes you feel worse. Afterward, not only does the original emotional issue remain, but you also feel guilty for overeating.
Occasionally using food as a pick-me-up, a reward, or to celebrate isn’t necessarily a bad thing. But when eating is your primary emotional coping mechanism—when your first impulse is to open the refrigerator whenever you’re stressed, upset, angry, lonely, exhausted, or bored—you get stuck in an unhealthy cycle where the real feeling or problem is never addressed.
Emotional hunger can’t be filled with food. Eating may feel good in the moment, but the feelings that triggered the eating are still there. And you often feel worse than you did before because of the unnecessary calories you’ve just consumed. You beat yourself for messing up and not having more willpower.
Compounding the problem, you stop learning healthier ways to deal with your emotions, you have a harder and harder time controlling your weight, and you feel increasingly powerless over both food and your feelings. But no matter how powerless you feel over food and your feelings, it is possible to make a positive change. You can learn healthier ways to deal with your emotions, avoid triggers, conquer cravings, and finally put a stop to emotional eating.
Before you can break free from the cycle of emotional eating, you first need to learn how to distinguish between emotional and physical hunger. This can be trickier than it sounds, especially if you regularly use food to deal with your feelings.
Emotional hunger can be powerful, so it’s easy to mistake it for physical hunger. But there are clues you can look for to help you tell physical and emotional hunger apart.
Emotional hunger comes on suddenly. It hits you in an instant and feels overwhelming and urgent. Physical hunger, on the other hand, comes on more gradually. The urge to eat doesn’t feel as dire or demand instant satisfaction (unless you haven’t eaten for a very long time).
Emotional hunger craves specific comfort foods. When you’re physically hungry, almost anything sounds good—including healthy stuff like vegetables. But emotional hunger craves junk food or sugary snacks that provide an instant rush. You feel like you need cheesecake or pizza, and nothing else will do.
Emotional hunger often leads to mindless eating. Before you know it, you’ve eaten a whole bag of chips or an entire pint of ice cream without really paying attention or fully enjoying it. When you’re eating in response to physical hunger, you’re typically more aware of what you’re doing.
Emotional hunger isn’t satisfied once you’re full. You keep wanting more and more, often eating until you’re uncomfortably stuffed. Physical hunger, on the other hand, doesn’t need to be stuffed. You feel satisfied when your stomach is full.
Emotional hunger isn’t located in the stomach. Rather than a growling belly or a pang in your stomach, you feel your hunger as a craving you can’t get out of your head. You’re focused on specific textures, tastes, and smells.
Emotional hunger often leads to regret, guilt, or shame. When you eat to satisfy physical hunger, you’re unlikely to feel guilty or ashamed because you’re simply giving your body what it needs. If you feel guilty after you eat, it’s likely because you know deep down that you’re not eating for nutritional reasons.

The first step in putting a stop to emotional eating is identifying your personal triggers. What situations, places, or feelings make you reach for the comfort of food? Most emotional eating is linked to unpleasant feelings, but it can also be triggered by positive emotions, such as rewarding yourself for achieving a goal or celebrating a holiday or happy event.
Common causes of emotional eating
Stress. Ever notice how stress makes you hungry? It’s not just in your mind. When stress is chronic, as it so often is in our chaotic, fast-paced world, your body produces high levels of the stress hormone, cortisol. Cortisol triggers cravings for salty, sweet, and fried foods—foods that give you a burst of energy and pleasure. The more uncontrolled stress in your life, the more likely you are to turn to food for emotional relief.
Stuffing emotions. Eating can be a way to temporarily silence or “stuff down” uncomfortable emotions, including anger, fear, sadness, anxiety, loneliness, resentment, and shame. While you’re numbing yourself with food, you can avoid the difficult emotions you’d rather not feel.
Boredom or feelings of emptiness. Do you ever eat simply to give yourself something to do, to relieve boredom, or as a way to fill a void in your life? You feel unfulfilled and empty, and food is a way to occupy your mouth and your time. In the moment, it fills you up and distracts you from underlying feelings of purposelessness and dissatisfaction with your life.
Childhood habits. Think back to your childhood memories of food. Did your parents reward good behavior with ice cream, take you out for pizza when you got a good report card, or serve you sweets when you were feeling sad? These habits can often carry over into adulthood. Or your eating may be driven by nostalgia—for cherished memories of grilling burgers in the backyard with your dad or baking and eating cookies with your mom.
Social influences. Getting together with other people for a meal is a great way to relieve stress, but it can also lead to overeating. It’s easy to overindulge simply because the food is there or because everyone else is eating. You may also overeat in social situations out of nervousness. Or perhaps your family or circle of friends encourages you to overeat, and it’s easier to go along with the group.
You probably recognized yourself in at least a few of the previous descriptions. But even so, you’ll want to get even more specific. One of the best ways to identify the patterns behind your emotional eating is to keep track with a food and mood diary.
Every time you overeat or feel compelled to reach for your version of comfort food Kryptonite, take a moment to figure out what triggered the urge. If you backtrack, you’ll usually find an upsetting event that kicked off the emotional eating cycle. Write it all down in your food and mood diary: what you ate (or wanted to eat), what happened to upset you, how you felt before you ate, what you felt as you were eating, and how you felt afterward.
Over time, you’ll see a pattern emerge. Maybe you always end up gorging yourself after spending time with a critical friend. Or perhaps you stress eat whenever you’re on a deadline or when you attend family functions. Once you identify your emotional eating triggers, the next step is identifying healthier ways to feed your feelings.
If you don’t know how to manage your emotions in a way that doesn’t involve food, you won’t be able to control your eating habits for very long. Diets so often fail because they offer logical nutritional advice which only works if you have conscious control over your eating habits. It doesn’t work when emotions hijack the process, demanding an immediate payoff with food.
In order to stop emotional eating, you have to find other ways to fulfill yourself emotionally. It’s not enough to understand the cycle of emotional eating or even to understand your triggers, although that’s a huge first step. You need alternatives to food that you can turn to for emotional fulfillment.
Alternatives to emotional eating

If you’re depressed or lonely, call someone who always makes you feel better, play with your dog or cat, or look at a favorite photo or cherished memento.
If you’re anxious, expend your nervous energy by dancing to your favorite song, squeezing a stress ball, or taking a brisk walk.
If you’re exhausted, treat yourself with a hot cup of tea, take a bath, light some scented candles, or wrap yourself in a warm blanket.
If you’re bored, read a good book, watch a comedy show, explore the outdoors, or turn to an activity you enjoy (woodworking, playing the guitar, shooting hoops, scrapbooking, etc.).
Most emotional eaters feel powerless over their food cravings. When the urge to eat hits, it’s all you can think about. You feel an almost unbearable tension that demands to be fed, right now! Because you’ve tried to resist in the past and failed, you believe that your willpower just isn’t up to snuff. But the truth is that you have more power over your cravings than you think.
Take 5 before you give in to a craving
Emotional eating tends to be automatic and virtually mindless. Before you even realize what you’re doing, you’ve reached for a tub of ice cream and polished off half of it. But if you can take a moment to pause and reflect when you’re hit with a craving, you give yourself the opportunity to make a different decision.
Can you put off eating for five minutes? Or just start with one minute. Don’t tell yourself you can’t give in to the craving; remember, the forbidden is extremely tempting. Just tell yourself to wait.
While you’re waiting, check in with yourself. How are you feeling? What’s going on emotionally? Even if you end up eating, you’ll have a better understanding of why you did it. This can help you set yourself up for a different response next time.
While it may seem that the core problem is that you’re powerless over food, emotional eating actually stems from feeling powerless over your emotions. You don’t feel capable of dealing with your feelings head on, so you avoid them with food.
Allowing yourself to feel uncomfortable emotions can be scary. You may fear that, like Pandora’s box, once you open the door you won’t be able to shut it. But the truth is that when we don’t obsess over or suppress our emotions, even the most painful and difficult feelings subside relatively quickly and lose their power to control our attention.
To do this you need to become mindful and learn how to stay connected to your moment-to-moment emotional experience. This can enable you to rein in stress and repair emotional problems that often trigger emotional eating. HelpGuide’s free Emotional Intelligence Toolkit can show you how.
When you eat to feed your feelings, you tend to do so quickly, mindlessly consuming food on autopilot. You eat so fast you miss out on the different tastes and textures of your food—as well as your body’s cues that you’re full and no longer hungry. But by slowing down and savoring every bite, you’ll not only enjoy your food more but you’ll also be less likely to overeat.
Slowing down and savoring your food is an important aspect of mindful eating, the opposite of mindless, emotional eating. Try taking a few deep breaths before starting your food, putting your utensils down between bites, and really focusing on the experience of eating. Pay attention to the textures, shapes, colors and smells of your food. How does each mouthful taste? How does it make your body feel?
By slowing down in this way, you’ll find you appreciate each bite of food much more. You can even indulge in your favorite foods and feel full on much less. It takes time for the body’s fullness signal to reach your brain, so taking a few moments to consider how you feel after each bite—hungry or satiated—can help you avoid overeating.

Eating while you’re also doing other things—such as watching TV, driving, or playing with your phone—can prevent you from fully enjoying your food. Since your mind is elsewhere, you may not feel satisfied or continue eating even though you’re no longer hungry. Eating more mindfully can help focus your mind on your food and the pleasure of a meal and curb overeating. See Mindful Eating.
Support yourself with healthy lifestyle habits
When you’re physically strong, relaxed, and well rested, you’re better able to handle the curveballs that life inevitably throws your way. But when you’re already exhausted and overwhelmed, any little hiccup has the potential to send you off the rails and straight toward the refrigerator. Exercise, sleep, and other healthy lifestyle habits will help you get through difficult times without emotional eating.

Authors: Melinda Smith, M.A., Lawrence Robinson, Jeanne Segal Ph.D., and Robert Segal, M.A.

Creative projects involving group work - general musical performance or group painting, collage, sculpture - are useful in helping to explore and strengthen social...
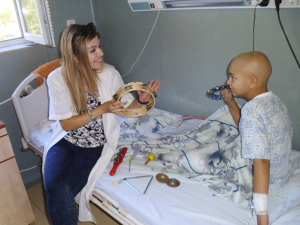
In the ARTON Program our team of oncopsychologists, art therapists and music therapists develops the process of children's creativity as a process of...

In ARTON sessions, creating a piece of music or a song is an emotional experience of coping and satisfaction for the participating children. They make friends with...

Painting provides patients with a spontaneous, plastic method of depicting thoughts and experiences. Painting with paints is not as structured as with pencil or...










